New Delhi: Researchers at the S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences have identified a new alloy with significant potential as a magnetic refrigerant, offering an eco-friendly and energy-efficient alternative to traditional cooling agents. This discovery could play a crucial role in minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and meeting the global demand for sustainable cooling technologies.
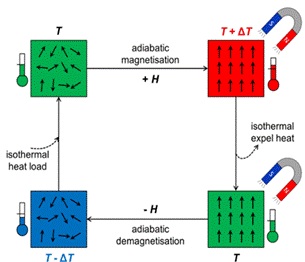
Magnetic refrigeration, as an alternative to the widely-used vapor-cycle refrigeration, is gaining attention for its energy efficiency and environmental benefits. The research team focused on developing new magnetic materials capable of serving as efficient refrigerants. The alloy in question, belonging to the all-transition metal-based Heusler alloys category, exhibited giant reversible magnetic cooling effects (MCE) and magneto-resistance (MR) under applied magnetic fields.
The Ni35Co15Mn34.5−xCuxTi15.5 alloy, specifically with copper (Cu) doping in the manganese (Mn) site, demonstrated remarkable properties. The addition of Cu modified the magnetic transition, enhancing the material’s metallic character while weakening the magnetic exchange interaction. This resulted in a substantial change in electrical resistance.
The researchers highlighted three critical criteria for magnetic materials in refrigeration applications: resistance to fatigue and failure, high thermal conductivity, and responsiveness to magnetic fields. The alloy under investigation showed giant reversible MCE and MR under a 5 T and 7 T magnetic field, surpassing reported values in the all-d-metal Heusler family.
The synergistic combination of significant MCE and MR in Cu-doped Heusler alloys opens avenues for various solid-state technological applications. The breakthrough holds promise for advancing eco-friendly cooling technologies and contributing to global efforts in energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. The research findings were published in the journal Physical Review Materials.